Structural steel connection design for tensile rupture by advanced inelastic analysis (AISC)
Connections are critical in structural steel buildings for transferring forces from member to member. Connections must be designed for safety and to ensure they serve their intended function.
Many resources are available to engineers for designing connections with common configurations and loads. However, connection designers often encounter configurations and loading conditions for which there is little guidance. In these cases, design by advanced inelastic analysis can be particularly advantageous.
IDEA StatiCa is a steel connection design software for design by advanced inelastic analysis. In this software, some limit states are captured in the same manner as standard strength equations, while others are not.
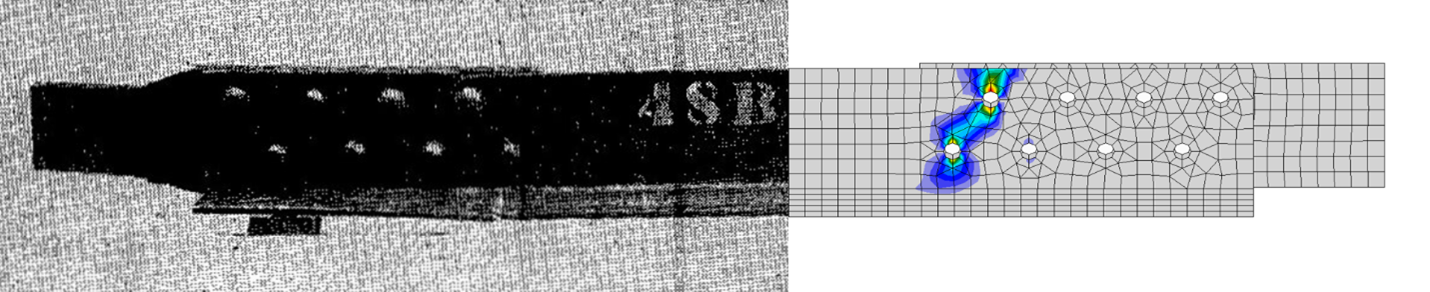
The net-section tensile rupture limit state is among the most basic limit states not captured using standard strength equations. It is not necessary to use standard strength equations in design by advanced inelastic analysis if the analysis provides a comparable or higher level of reliability.
To date, no rigorous reliability analysis has been performed to show IDEA StatiCa, and the underlying component-based finite element method, provide a comparable or higher level of reliability than provided by the standard strength equations. Such a reliability analysis is performed in this work for the limit state of tensile rupture.
Data from hundreds of previously published experimental results exhibiting tensile rupture in a variety of connection types were examined and analyzed. Strengths from both standard equations and IDEA StatiCa were compared to the experimentally obtained strengths and to each other. A reliability analysis based on Monte Carlo simulations was conducted using results from the strength comparisons. Additionally, the sensitivity of the IDEA StatiCa strength to mesh parameters and plastic strain limit was quantified.
The results indicate that IDEA StatiCa does, in most cases, provide a comparable or higher level of reliability than the standard strength equations. Cases where it does not are identified, and options for modifications are recommended.
Documentation of the level of safety provided by IDEA StatiCa for the tensile rupture limit state presented in this work will bring confidence to the overall approach and enable the wider use of this helpful tool.