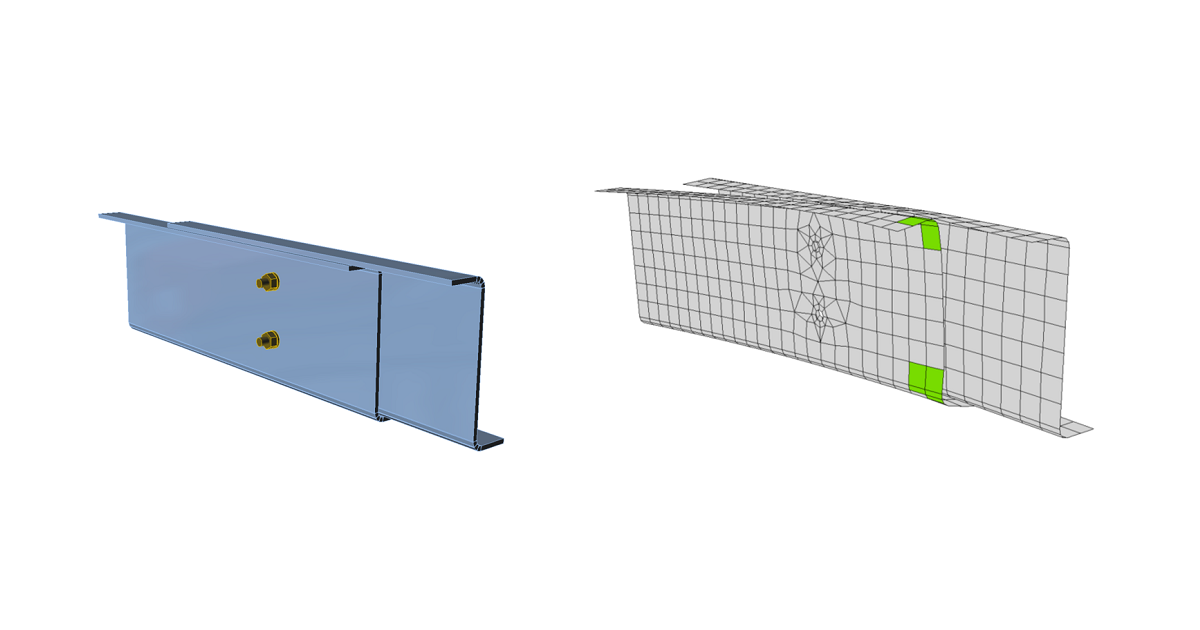
Code-check of plates according to Hong Kong Code
The resulting equivalent stress (HMH, von Mises) and plastic strain are calculated on plates. When the design yield strength, \(p_y\) (Cl. 3.1.2), on the bilinear material diagram is reached, the check of the equivalent plastic strain is performed. The limit value of 5 % is suggested in Eurocode (EN 1993-1-5 App. C, Par. C8, Note 1). This value can be modified in Code setup but verification studies were made for this recommended value.
Plate element is divided into five layers, and elastic/plastic behavior is investigated in each. The program shows the worst result of all of them.
Stress may be a little bit higher than the design yield strength. The reason is the slight inclination of the plastic branch of the stress-strain diagram, which is used in the analysis to improve the stability of the calculation.
\[ p_y = \min \left \{ \frac{Y_s}{\gamma_{m1}}, \frac{U_s}{\gamma_{m2}} \right \} \]
where:
- \(p_y\) – design yield strength
- \(Y_s\) – characteristic yield strength
- \(U_s\) – minimum tensile strength
- \(\gamma_{m1}\) – material factor (Table 4.1); default value \(\gamma_{m1} = 1\) editable in Code setup
- \(\gamma_{m2}\) – material factor (Table 4.1); default value \(\gamma_{m2} = 1.2\) editable in Code setup