Bolt bearing distances for Eurocode
The new version brings an improved algorithm for calculating the bolt spacing (p1; p2), end (e1), and edge (e2) distances for the Eurocode bearing check. This improvement is mostly relevant for general plate geometries, plates with openings, cutouts, etc.
The algorithm reads the real direction of the resulting shear force vector in a given bolt and then calculates the distances needed for the bearing check.
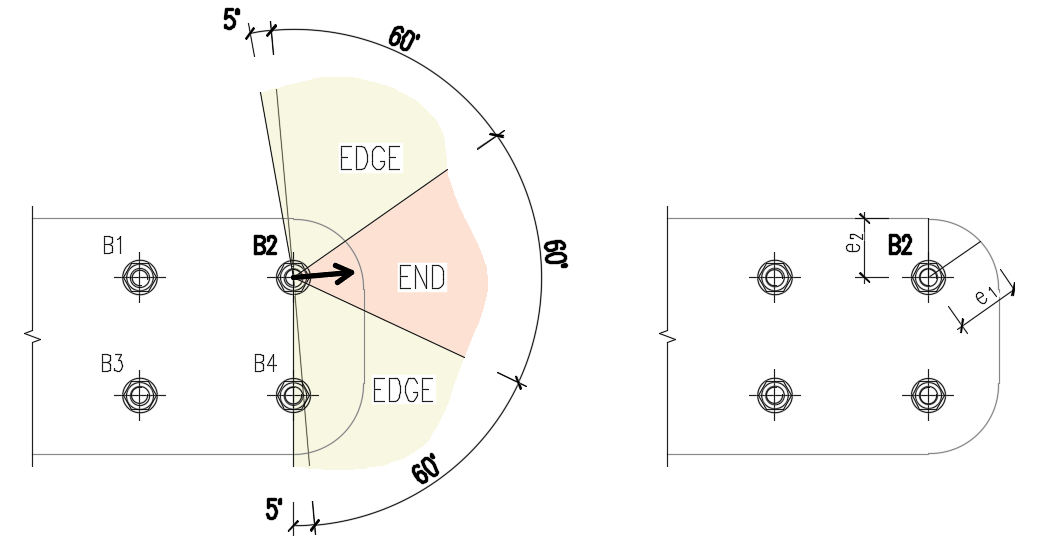
The end (e1) and edge (e2) distances are determined by dividing the plate contour into three segments. The "end segment" is indicated by a 60° range in the direction of the force vector. The "edge segments" are defined by two 65° ranges perpendicular to the force vector. The shortest distance between a bolt and an edge in the relevant segment is then taken as an end, or edge distance.
The algorithm evaluates all plates connected by the bolt—the connecting plates (e.g., a splice plate), the member plates (e.g., a top flange), and the shortest distance is used.
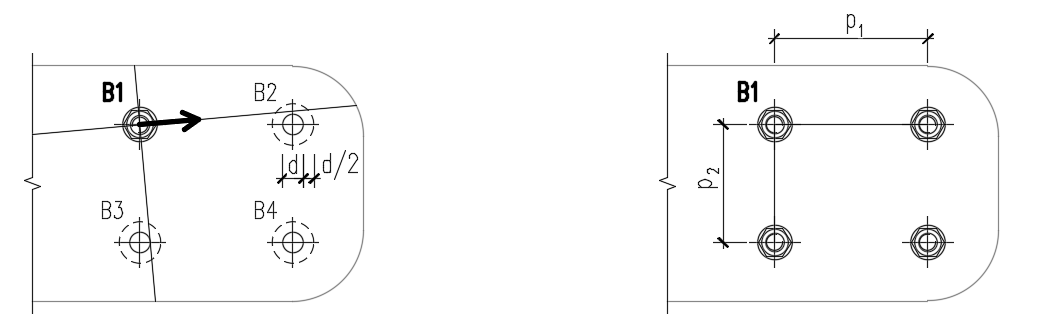
The spacing distances between bolt holes (p1; p2) are determined by virtually enlarging the surrounding bolt holes by half their diameter, then drawing two lines in the direction and perpendicular to the shear force vector. When these lines intersect with virtually enlarged bolt holes, then the distances to these bolts are considered as p1 and p2 in the calculation.
If the lines don't intersect with the visually closest bolt (even though the line misses the bolt closely), this bolt is neglected. If the lines don't intersect with any bolt, an infinite value is used.
Available in Expert and Enhanced editions.